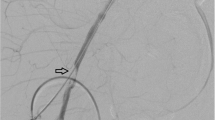
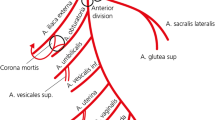
Abstract
There has been an increasing demand for interventional radiology (IR) procedures for the treatment of severe postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) (also called critical hemorrhage in obstetrics). The Japanese Society of Interventional Radiology Guideline Committee developed the practical guidelines for IR procedures for severe PPH using evidence-based methodology. This article aimed to describe the rationale for developing these guidelines and to provide the answers for clinical questions about IR procedures consisting of current available evidence and the consensus among experts.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) remains one of the leading causes of maternal morality. Severe PPH (also called critical hemorrhage in obstetrics) accounts for approximately 25 % of maternal mortality worldwide and more than 30 % in some of the developing countries [1]. Moreover, morbidity is increasing even in the developed, highly resourced countries, although mortality is decreasing. Life-threatening severe PPH occurs in 1/300 pregnancies, with increased risks for patients with placental abnormalities, previous history of cesarean section, and multiple pregnancy. The essential treatment for severe PPH is blood transfusion to replenish deficiencies from blood loss. To stop bleeding, nonsurgical compression (e.g., bimanual compression and balloon tamponade) and surgical compression (e.g., B-lynch suture) have been widely used. Surgical arterial ligation using step-wise devascularization has also been used; however, interventional radiology techniques have been recognized as alternatives to surgery in the past 2 decades [2, 4].
The Japanese Society of Interventional Radiology (JSIR) has engaged in the production of practical guidelines for interventional radiology (IR) procedures since 2008. The purpose of these guidelines is to provide aid to physicians who perform interventional procedures in various settings. In 2009, a task force on the use of interventional radiology for severe PPH was launched to develop, update, and revise guidelines. The task force published the first version of these guidelines in October 2012.
Development of the guidelines
Task force composition
The JSIR Guidelines Committee convened an Expert Task Force consisting of nine interventional radiologists and three obstetrical specialists. For the external review, an Expert Task Force for External Evaluation was organized with one interventional radiologist and six obstetrical specialists.
Evidence-based guideline development process
Clinical questions were developed for the emergency use of IR for PPH and the prophylactic use of IR prior to surgery for placental abnormalities. A literature search was performed using MEDLINE (PubMed) and ICHUSHI (for Japanese literature) with date parameters of January 1983 through September 2009. Additional searches were performed until the task force had completely determined the recommendations in October 2010. Two search formulas were set: {(“postpartum hemorrhage”) and (therapy) and (embolization) and English [lang]} for emergency interventions for PPH and {(“placenta accreta” or “placenta previa”) and (embolization or occlusion) and English [lang])} for prophylactic intervention for the surgery of placental abnormalities. Literatures in Japanese were also searched with similar formulas. Studies were included if they included indications, technical details, or the safety and efficacy data of IR for PPH. A structured abstract was made for each document included, and the level of evidence was identified according to the definition by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). Structured abstracts were reviewed by the members of the Task Force. Answers for each clinical question were developed according to the evidence from the literature and consensus among the members. The JSIR Guideline Committee reviewed and approved the content and the text of the guideline. Feedback from the External Evaluation Committee was solicited, and public comments were sought through the web page of JSIR before publication.
Target audience
The target audience of this guideline was determined to be physicians who perform IR for PPH.
Guideline and conflicts of interest
Members of the Task Force had no conflicts of interest regarding the contents of this guideline.
Questionnaire survey
To reveal the current status of the use of IR for PPH, a questionnaire survey was sent to 75 tertiary perinatal centers in January 2012. A total of 48 (64 %) obstetricians and 48 (64 %) radiologists responded to the questionnaire. Following are the main results.
-
1.
Recognition of IR for PPH among obstetricians.
A total of 46 obstetricians (96 %) already knew IR can be used for PPH.
-
2.
Number of IR procedures for PPH in past 5 years.
Thirty-six institutions (75 %) had experience with emergency IR and 20 (41 %) had experience with prophylactic IR. With regard to prophylactic IR, arterial embolization was performed in 25 % and preoperative insertion of balloon catheters in 46 % of the 20 institutions.
-
3.
Number of physicians providing IR procedures.
In 42 institutions (87 %), IR procedures were performed by radiologists. Of those institutions, 75 % had more than two radiologists performing IR procedures.
-
4.
Indications for IR.
Emergency IR was indicated when “massive bleeding was seen and the patient was hemodynamically stable” in 81 % of the institutions. Prophylactic IR was indicated for “abnormal placentation with the potential to cause massive bleeding during surgery” in 44 % and for “all cases before the surgery for abnormal placentation” in 21 % of institutions.
Literature review results
A total of 160 documents written in English and 74 in Japanese were identified for emergency IR. For prophylactic IR, 86 documents in English and 90 in Japanese were identified.
Clinical questions and answers
CQ 1
What is the status of emergency IR for PPH?
Answer 1
Physicians who are able to perform IR procedures should consider arterial embolization for severe PPH.
(Grade C1)
Specific comments
There is no evidence regarding the superiority of IR over other methods for the treatment of severe PPH. In addition, institutional and regional differences in the availability of IR have to be taken into account.
Given that pregnant women are vulnerable to disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), delaying hemostatic treatment may lead to the development of DIC, which can be life threatening. The primary principle for developing a therapeutic strategy is to choose the most prompt and reliable hemostatic method. The advantages of IR compared to surgical hemostasis are prompt hemostasis with minimal invasion, repeatability, and conservation of fertility. If emergency IR is available, IR should be considered as a first choice of hemostatic measure for PPH. However, the conversion to surgical hemostasis should be discussed when IR is not effective. Prompt and appropriate decision-making is essential for saving life, which is based on having good communication among the interventional radiologist, obstetrician, and anesthetist.
The following are causes of PPH for which IR may be indicated.
-
1.
Uterine atony (the most frequent cause of PPH).
-
2.
Retained placenta.
-
3.
Placenta previa.
-
4.
Uterine inversion.
-
5.
Laceration of the birth canal (uterine rupture, cervical laceration).
-
6.
Postoperative bleeding.
CQ 2
How should we perform the emergency IR procedure for PPH?
Answers 2
-
1.
Pelvic arteriogram with a catheter tip above the origin of the ovarian arteries or internal iliac arteriogram is first performed.
-
2.
Selective embolization is considered in the presence of extravasation.
-
3.
Embolization of the bilateral uterine arteries is performed in the absence of extravasation at angiography.
-
4.
Embolization of the bilateral anterior division of the internal iliac artery is performed if bilateral uterine arterial embolization is impossible or fails to stop the bleeding.
-
5.
Search for other bleeding sources with arteriography from the abdominal aorta or the external iliac arteries if bilateral internal iliac arterial embolization fails.
-
6.
Gelatin sponge particle is recommended as an embolic material for embolization of the uterine artery or the internal iliac artery.
(Grade C1)
Specific comments
Use of an angiographic suite equipped with digital subtraction angiography (DSA) with fluoroscopy of adequate image quality to visualize a microcatheter is recommended. The common femoral artery is recommended as a puncture site. Pelvic aortography is performed to assess the arterial anatomy and identify the bleeding origin; however, this process can be omitted depending on the patients’ vital status and operator’s experience.
Functional bleeding, including uterine atony, DIC, uterine inversion, and placenta-related bleeding, may not be indicated for superselective embolization because of multiple bleeding points. The bilateral uterine arteries or anterior division of the internal iliac arteries are embolized in such cases. Superselective embolization may be considered in the presence of extravasation at angiography caused by pseudoaneurysm or active bleeding from lacerations and/or tears of the genital tract. However, visualization of extravasation on angiography ranges from 21 to 93 % [5–10]. When extravasation is not identified, embolization can be performed from bilateral uterine arteries or the internal iliac arteries. The level of embolization has to be determined according to the urgency and time constraints in any bleeding pathogenesis.
The gelatin sponge particle is the most common embolic agent [5, 11, 12]. The fine particle-like gelatin powder is not recommended because of the risk of adverse events associated with tissue ischemia, including the uterus and other pelvic organs, nerves, and the soft tissues [13, 14]. The preferred preparation method of the gelatin sponge is the hand-cut method. The pumping method is quick but should be chosen only for critical situations because of its higher risk of ischemic complications, since the size is not uniform and smaller-sized particles are used [14]. Pre-formed particles of ~1 mm can also be considered. A mixture of N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate (NBCA) and Lipiodol® may be selected for cases of DIC, recanalization after use of a gelatin sponge, and pseudoaneurysm for robust and permanent coagulation by polymerization. Polyvinyl alcohol is also used although it has not yet been approved in Japan [9].
CQ 3
What is the clinical success rate of emergency IR for PPH?
Answers 3
-
1.
The clinical success rate for arterial embolization is approximately 90 %.
-
2.
Hysterectomy, after failure of TAE for PPH, occurs in approximately 8 % of patients after IR.
-
3.
The mortality after arterial embolization (including that after surgery) is ≤2 %.
(Grade C1)
Specific comments
The definition of the clinical success of emergency transcatheter arterial embolization (TAE) for PPH is the achievement of successful hemostasis without the need for subsequent surgical hemostatic treatment [3, 15, 16]. The success rate is influenced by the patient’s condition, including the hemodynamics and coagulation system factors, as well as a history of prior surgery. The reported clinical success rates of TAE for PPH range from 71.5 to 100 % [5, 15]. Seven papers described failed TAE followed by hysterectomy [3, 17]. The failure rate for TAE ranges from 4 to 12 %.
A limited number of studies have analyzed the correlation between the causes of PPH and the clinical success rates. The clinical success rate for TAE of atonic bleeding is reported to be 88 %, which is the highest success rate for TAE among the different causes of PPH [15]. However, the clinical success rate of TAE of a genital tract laceration is reported to be 45 %, whereas that after hemorrhagic shock is reported to be 39 % [15]. The possible factors responsible for clinical failure include a history of prior surgery, spasm of the arteries, unilateral embolization, proximal embolization, and DIC. The success rate of secondary intervention is high (up to 80 %).
The occurrence of death after TAE is rare, and only 0 to 2 cases have been noted in each paper. The causes of death were reported to be DIC, multi-organ failure, and cerebral hemorrhage. Fatal complications directly attributable to TAE have not been reported.
CQ 4
What are the complications of emergency IR for PPH?
Answers 4
-
1.
Complications may develop in 6–7 % of patients after emergency arterial embolization.
-
2.
Severe complications, such as those requiring hysterectomy, occur in less than 1.6 % of patients.
-
3.
Post-embolization syndrome may occur.
(Grade C1)
Specific comments
In this section, the previously reported complications are categorized according to the definitions of the Society of Interventional Radiology (SIR) Standards of Practice Committee’s Classification of Complications.
-
1.
Minor complications
-
a.
No need for specific therapy, no consequences [8, 11, 25, 26]. Hematoma at the puncture site, arterial dissection (minor), post-embolization syndrome, embolization of non-targeted arteries such as ischemia of the lumber nerve plexus, allergy to local anesthetic (minor).
-
b.
Nominal therapy, no consequences: includes overnight admission only. Injury of the iliac artery and/or its branches, allergy to contrast material.
-
a.
-
2.
Major complications
-
a.
Requirement of minor therapy, minor hospitalization (<48 h) [15, 27, 28]. Pelvic infection, uterine ischemia, lumbar nerve ischemia caused by non-targeted embolization such as necrosis of pelvic organs (e.g., bladder, intestine, or vagina), and distal arterial embolism.
-
b.
Require major therapy, unplanned increase in level of care, prolonged hospitalization (>48 h) [15, 19, 26, 29–31]. Retroperitoneal hemorrhage, endometritis, endometrial infection, vaginal necrosis, bladder necrosis, limb ischemia, muscle necrosis, cardiac pulmonary edema due to massive hemorrhage, transient renal failure.
-
c.
Permanent adverse sequelae [13, 30, 32–34]. Uterine necrosis, vaginal fistula, Asherman syndrome.
-
d.
Death [15, 17]. Four fatal cases have been reported. The causes of death were cerebral hemorrhage (n = 2) and excessive bleeding (n = 2). There has been no fatal case caused directly by TAE.
-
a.
CQ 5
How does emergency IR affect on fertility?
Answers 5
-
1.
The menstrual cycle resumes in 91–100 % of women after TAE. More than 78 % of them exhibit a normal cycle.
-
2.
Successful pregnancy is reported in 79 % of women with preserved fertility.
-
3.
Asherman syndrome may be caused by the use of smaller particles (less than 500 microns).
-
4.
Women with a history of uterine artery embolization have a higher risk of PPH in subsequent pregnancies, at a rate of ~14 %.
(Grade B)
Specific comments
The priority of IR for PPH is hemostasis; however, the issue of preserving fertility cannot be ignored. The menstrual cycle resumes in 91–100 % of patients who have undergone emergency TAE [1, 11, 15, 17, 20, 35–39]. Pregnancy can be expected in 69–100 % (average, 79 %) of women who desire future pregnancy [35]. A high cesarean section rate of 62 % (approximately 3-fold that of the general population) is reported in women with a history of TAE [35]; however, this high rate of cesarean section may be attributable to a prophylactic indication against repeated PPH. Incidences of placental abnormality (15 %) and recurrent PPH (14 %) are also higher in women with a history of TAE than in the general population [40].
CQ 6
Which women are indicated for prophylactic IR prior to cesarean delivery?
Answers 6
-
1.
Women with an increased risk of intraoperative massive bleeding based on suspected placental abnormalities (placenta accreta/increta/percreta).
-
2.
Any conditions prone to severe intraoperative bleeding.
(Grade C1)
Specific comments
There is no evidence regarding the efficacy of prophylactic IR on patients with an increased risk of massive bleeding at delivery. Thus, this indication is still controversial [32, 41–48]. Patients with fibroids and multiple pregnancies may be indicated for prophylactic IR, though only three cases with successful bleeding control have been reported.
CQ 7
How should we perform prophylactic IR prior to surgery in women with abnormal placentation?
Answers 7
-
1.
Insertion of balloon catheters into the common iliac arteries or the internal iliac arteries is considered before cesarean section.
-
2.
Arterial embolization is considered after the delivery of the baby.
(Grade C1)
Specific comments [22, 26, 32, 41–48]
-
1.
Insertion of occlusion balloon catheters: To reduce bleeding during cesarean section, two balloon catheters are advanced from the femoral arteries to the contralateral iliac arteries prior to a planned cesarean section or hysterectomy. The contralateral approach is chosen to prevent possible severe ischemia of the lower extremities due to the migration of balloon catheters into the external iliac arteries by blood flow. The position of the balloon catheter is controversial as to whether the common iliac artery or the internal iliac artery is the appropriate position for the balloon occlusion. If the balloon catheters are inflated while the fetus is in utero, careful observation of the fetal heart rate is mandatory in order to monitor possible adverse events due to a decrease in the blood flow.
-
2.
Arterial embolization. Arterial embolization from the uterine arteries or the internal iliac arteries can be performed instead of balloon occlusion or after balloon occlusion. The preference of a two-stage or a simultaneous cesarean delivery and hysterectomy (ceserian hysterectomy) varies by institution.
CQ 8
What is the clinical success rate for prophylactic IR prior to surgery in women with abnormal placentation?
Answer 8
The clinical success rate for prophylactic IR, defined as the control of bleeding, is expected in 77–100 % of women.
Specific comments [22, 26, 32, 41–48]
Bleeding may be excessive in patients with placenta previa because hemostasis by uterine contraction is insufficient. Furthermore, placenta accreta may cause extraordinary massive bleeding during the procedure. The reported incidence of placental abnormalities in cesarean section deliveries is 25–40 %. The importance of prophylactic IR is growing because abnormal placentation is increasingly frequent because of an increase in the number of previous cesarean sections, which have continued to rise in number. From the results of 78 articles identified in the literature search, the success rate ranges from 48 to 100 %. Excluding articles with a small number of patients (n < 10), the success rate is 77–100 %. However, the definition of “clinical success” varied by study, and the definitive efficacy of IR has not yet been determined because of a lack of comparative studies.
CQ 9
What are the complications of prophylactic IR prior to surgery in women with abnormal placentation?
Answers 9
-
1.
Allergy to drugs (e.g., contrast material, local anesthetics).
-
2.
Hematoma at the puncture site.
-
3.
Vascular injury caused by catheter manipulation or balloon inflation.
-
4.
Arterial thromboembolism caused by balloon inflation.
-
5.
Postembolization syndrome, technical failure, and recanalization of the embolized vessel may occur.
-
6.
Radiation exposure.
(Grade C1)
Specific comments [22, 26, 32, 41–48]
Complications from prophylactic insertion of occlusion balloon catheters include angiography, thromboembolic events, and damaged balloons resulting in the failure of efficient occlusion of the arteries. The safe radiation dose for the fetus has not been reported; however, the reported fluoroscopy time was less than 5 min; thus, the dose is estimated as <50 mGy. Care should be taken to reduce radiation exposure.
CQ 10
What is the strategy for patients with an allergy to iodized contrast material?
Answers 10
-
1.
Consider other treatments.
-
2.
In the absence of other treatments available for patients who face an increased risk of life-threatening bleeding, the following IR methods are applicable.
-
(1)
Use of iodized contrast material in an intensive care setting ideally attended by anesthesiologists.
-
(2)
Use of contrast material other than iodized contrast material.
-
(1)
(No grade)
Specific comments
There are no guidelines for the use of contrast material in emergency or serious conditions for patients with allergies to the contrast material. Thus, the strategy for patients with allergy to iodized contrast material should be determined on a case-by-case basis. Gadolinium-DTPA and CO2 are considered alternatives to iodized contrast material.
CQ 11
Is there any adverse effect on the mother and/or fetus from radiation exposure in endovascular treatment for PPH?
Answer 11
Radiation exposure dosages are small (with fewer adverse effects) in the mother and fetus during IR procedures for PPH.
(No grade)
Specific comments
Few studies have reported maternal and fetal radiation doses during IR for PPH. There are no available data on radiation doses during emergency arterial embolization. The radiation dose during a similar procedure, i.e., uterine artery embolization for symptomatic uterine leiomyoma, is reported to be 50–220 mGy to the ovaries and 450–1,600 mGy to the skin with 10–35 min fluoroscopic time [49, 50].
The fetus in utero may have a risk of radiation exposure during prophylactic insertion of occlusion balloon catheters. The maternal skin dose was 50–150 mGy in a setting of 3 min fluoroscopic time in this type of procedure [51]. Radiation exposure may possibly cause growth retardation during late pregnancy; however, this is unlikely to occur because the threshold dosage is estimated as >1,000 mGy. Carcinogenic effects from radiation exposure to the fetus or deteriorated ovarian function in the patient are also unlikely with adequate interventional procedures.
Attentive care should be taken to reduce radiation exposure as much as possible. To avoid unnecessary radiation exposure, dose minimization techniques should be employed as follows: pulsed fluoroscopy at a low pulse rate, the shortest length of fluoroscopic time, appropriate collimation, and use of the fluoroscopic image as the archive instead of digital subtraction angiography.
Conclusion
IR has become a treatment option for PPH. To perform IR procedures effectively and safely, radiologists should know the basic techniques as well as the complications and limitations of each IR procedure.
References
Al-Zirqi I, Vangen S, Forsen L, Stray-Pedersen B. Prevalence and risk factors of severe obstetric haemorrhage. BJOG. 2008;115:1265–72.
Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG). The role of emergency and elective interventional radiology in postpartum haemorrhage. 2007.
Mathe ML, Morau E, Vernhet-Kovacsik H, Picot MC, Boulot P. Impact of the new French clinical practice recommendations in embolization in postpartum and post-abortion hemorrhage: study of 48 cases. J Perinat Med. 2007;35:532–7.
Pelage JP, Le Dref O, Mateo J, Soyer P, Jacob D, Kardache M, et al. Life-threatening primary postpartum hemorrhage: treatment with emergency selective arterial embolization. Radiology. 1998;208:359–62.
Chung JW, Jeong HJ, Joh JH, Park JS, Jun JK, Kim SH. Percutaneous transcatheter angiographic embolization in the management of obstetric hemorrhage. J Reprod Med. 2003;48:268–76.
Deux JF, Bazot M, Le Blanche AF, Tassart M, Khalil A, Berkane N, et al. Is selective embolization of uterine arteries a safe alternative to hysterectomy in patients with postpartum hemorrhage? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;177:145–9.
Ratnam LA, Gibson M, Sandhu C, Torrie P, Chandraharan E, Belli AM. Transcatheter pelvic arterial embolisation for control of obstetric and gynaecological haemorrhage. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2008;28:573–9.
Shim JY, Yoon HK, Won HS, Kim SK, Lee PR, Kim A. Angiographic embolization for obstetrical hemorrhage: effectiveness and follow-up outcome of fertility. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2006;85:815–20.
Vegas G, Illescas T, Munoz M, Perez-Pinar A. Selective pelvic arterial embolization in the management of obstetric hemorrhage. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2006;127:68–72.
Yamashita Y, Harada M, Yamamoto H, Miyazaki T, Takahashi M, Miyazaki K, et al. Transcatheter arterial embolization of obstetric and gynaecological bleeding: efficacy and clinical outcome. Br J Radiol. 1994;67:530–4.
Boulleret C, Chahid T, Gallot D, Mofid R, Tran Hai D, Ravel A, et al. Hypogastric arterial selective and superselective embolization for severe postpartum hemorrhage: a retrospective review of 36 cases. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2004;27:344–8.
Cheng YY, Hwang JI, Hung SW, Tyan YS, Yang MS, Chou MM, et al. Angiographic embolization for emergent and prophylactic management of obstetric hemorrhage: a four-year experience. J Chin Med Assoc. 2003;66:727–34.
Chitrit Y, Zafy S, Pelage JP, Ledref O, Khoury R, Caubel P. Amenorrhea due to partial uterine necrosis after uterine artery embolization for control of refractory postpartum hemorrhage. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2006;127:140–2.
Katsumori T, Kasahara T. The size of gelatin sponge particles: differences with preparation method. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2006;29:1077–83.
Touboul C, Badiou W, Saada J, Pelage JP, Payen D, Vicaut E, et al. Efficacy of selective arterial embolisation for the treatment of life-threatening post-partum haemorrhage in a large population. PLoS ONE. 2008;3:e3819.
Brown BJ, Heaston DK, Poulson AM, Gabert HA, Mineau DE, Miller FJ Jr. Uncontrollable postpartum bleeding: a new approach to hemostasis through angiographic arterial embolization. Obstet Gynecol. 1979;54:361–5.
Chauleur C, Fanget C, Tourne G, Levy R, Larchez C, Seffert P. Serious primary post-partum hemorrhage, arterial embolization and future fertility: a retrospective study of 46 cases. Hum Reprod. 2008;23:1553–9.
Cheong JY, Kong TW, Son JH, Won JH, Yang JI, Kim HS. Outcome of pelvic arterial embolization for postpartum hemorrhage: a retrospective review of 117 cases. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2014;57:17–27.
Eriksson LG, Mulic-Lutvica A, Jangland L, Nyman R. Massive postpartum hemorrhage treated with transcatheter arterial embolization: technical aspects and long-term effects on fertility and menstrual cycle. Acta Radiol. 2007;48:635–42.
Fiori O, Deux JF, Kambale JC, Uzan S, Bougdhene F, Berkane N. Impact of pelvic arterial embolization for intractable postpartum hemorrhage on fertility. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009;200(384):e1–4.
Gilbert WM, Moore TR, Resnik R, Doemeny J, Chin H, Bookstein JJ. Angiographic embolization in the management of hemorrhagic complications of pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1992;166:493–7.
Hansch E, Chitkara U, McAlpine J, El-Sayed Y, Dake MD, Razavi MK. Pelvic arterial embolization for control of obstetric hemorrhage: a five-year experience. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999;180:1454–60.
Heaston DK, Mineau DE, Brown BJ, Miller FJ Jr. Transcatheter arterial embolization for control of persistent massive puerperal hemorrhage after bilateral surgical hypogastric artery ligation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1979;133:152–4.
Murakami R, Ichikawa T, Kumazaki T, Kobayashi Y, Ogura J, Kurokawa A. Transcatheter arterial embolization for postpartum massive hemorrhage: a case report. Clin Imaging. 2000;24:368–70.
Pelage JP, Soyer P, Repiquet D, Herbreteau D, Le Dref O, Houdart E, et al. Secondary postpartum hemorrhage: treatment with selective arterial embolization. Radiology. 1999;212:385–9.
Ojala K, Perala J, Kariniemi J, Ranta P, Raudaskoski T, Tekay A. Arterial embolization and prophylactic catheterization for the treatment for severe obstetric hemorrhage. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2005;84:1075–80.
Cordonnier C, Ha-Vien DE, Depret S, Houfflin-Debarge V, Provost N, Subtil D. Foetal growth restriction in the next pregnancy after uterine artery embolisation for post-partum haemorrhage. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2002;103:183–4.
van Nieuwkoop C, Tijsterman JD, Van Dissel JT. Gather ye buds: fungus formation of the bladder after complicated cesarean section. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;199(207):e1–2.
Breathnach F, Tuite DJ, McEniff N, Byrne P, Geary MP. Uterine artery embolisation as an interval adjunct to conservative management of placenta praevia increta. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2007;27:195.
Greenwood LH, Glickman MG, Schwartz PE, Morse SS, Denny DF. Obstetric and nonmalignant gynecologic bleeding: treatment with angiographic embolization. Radiology. 1987;164:155–9.
Maassen MS, Lambers MD, Tutein Nolthenius RP, van der Valk PH, Elgersma OE. Complications and failure of uterine artery embolisation for intractable postpartum haemorrhage. BJOG. 2009;116:55–61.
Clement D, Kayem G, Cabrol D. Conservative treatment of placenta percreta: a safe alternative. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2004;114:108–9.
Courbiere B, Jauffret C, Provansal M, Agostini A, Bartoli JM, Cravello L, et al. Failure of conservative management in postpartum haemorrhage: uterine necrosis and hysterectomy after angiographic selective embolization with gelfoam. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2008;140:291–3.
Porcu G, Roger V, Jacquier A, Mazouni C, Rojat-Habib MC, Girard G, et al. Uterus and bladder necrosis after uterine artery embolisation for postpartum haemorrhage. BJOG. 2005;112:122–3.
Berkane N, Moutafoff-Borie C. Impact of previous uterine artery embolization on fertility. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2010;22:242–7.
Delotte J, Novellas S, Koh C, Bongain A, Chevallier P. Obstetrical prognosis and pregnancy outcome following pelvic arterial embolisation for post-partum hemorrhage. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009;145:129–32.
Goldberg J, Pereira L, Berghella V. Pregnancy after uterine artery embolization. Obstet Gynecol. 2002;100:869–72.
Kirby JM, Kachura JR, Rajan DK, Sniderman KW, Simons ME, Windrim RC, et al. Arterial embolization for primary postpartum hemorrhage. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009;20:1036–45.
Salomon LJ, deTayrac R, Castaigne-Meary V, Audibert F, Musset D, Ciorascu R, et al. Fertility and pregnancy outcome following pelvic arterial embolization for severe post-partum haemorrhage. A cohort study. Hum Reprod. 2003;18:849–52.
Gaia G, Chabrot P, Cassagnes L, Calcagno A, Gallot D, Botchorishvili R, et al. Menses recovery and fertility after artery embolization for PPH: a single-center retrospective observational study. Eur Radiol. 2009;19:481–7.
Dubois J, Garel L, Grignon A, Lemay M, Leduc L. Placenta percreta: balloon occlusion and embolization of the internal iliac arteries to reduce intraoperative blood losses. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1997;176:723–6.
Mushtaq S, Kurdi W, Al-Shammari M. Prophylactic catheters placement and intraoperative internal iliac artery embolisation in a patient with placenta accreta. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2007;27:853–5.
Sewell MF, Rosenblum D, Ehrenberg H. Arterial embolus during common iliac balloon catheterization at cesarean hysterectomy. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;108:746–8.
Shih JC, Liu KL, Shyu MK. Temporary balloon occlusion of the common iliac artery: new approach to bleeding control during cesarean hysterectomy for placenta percreta. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;193:1756–8.
Timmermans S, van Hof AC, Duvekot JJ. Conservative management of abnormally invasive placentation. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2007;62:529–39.
Tseng SH, Lin CH, Hwang JI, Chen WC, Ho ES, Chou MM. Experience with conservative strategy of uterine artery embolization in the treatment of placenta percreta in the first trimester of pregnancy. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2006;45:150–4.
Weeks SM, Stroud TH, Sandhu J, Mauro MA, Jaques PF. Temporary balloon occlusion of the internal iliac arteries for control of hemorrhage during cesarean hysterectomy in a patient with placenta previa and placenta increta. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2000;11:622–4.
Winograd RH. Uterine artery embolization for postpartum hemorrhage. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2008;22:1119–32.
Glomset O, Hellesnes J, Heimland N, Hafsahl G, Smith HJ. Assessment of organ radiation dose associated with uterine artery embolization. Acta Radiol. 2006;47:179–85.
Tse G, Spies JB. Radiation exposure and uterine artery embolization: current risks and risk reduction. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010;13:148–53.
Toda J, Kimra T, Tsuchiya A, Sakai M, Masaoka N, Ihmuro M. Caesarian section under balloon occlusion of the bilateral interanal iliac arteries in patients with high risk pregnancy. IVR: interventional. Radiology. 2009;24:134–7.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This report describes the current guidelines for interventional radiology for postpartum hemorrhage published online in Japanese at the web site of the Japanese Society of Interventional Radiology in 2012 (http://www.jsivr.jp/guideline/guideline_2012sanka.html).
About this article
Cite this article
Sone, M., Nakajima, Y., Woodhams, R. et al. Interventional radiology for critical hemorrhage in obstetrics: Japanese Society of Interventional Radiology (JSIR) procedural guidelines. Jpn J Radiol 33, 233–240 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-015-0399-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-015-0399-0